How to do Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) in Odoo
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a set of good practices to optimize your website so that you get a better ranking in search engines like Google. In short, a good SEO allows you to get more visitors.
Some examples of SEO rules: your web pages should load fast, your page
should have one and only one title <h1>, meta tags
(alt-tag, title-tag) should be
consistent with the content, your website should have a
/sitemap.xml file, etc.
To guarantee Odoo Website and Odoo eCommerce users have a great SEO, Odoo abstracts all the technical complexities of SEO and handles everything for you, in the best possible way. This will be explained here below.
But first, let see how you can easily boost your ranking by finetuning the content and the meta tags of your website.
Meta Tags
Title, Description
Every web page should define the <title> and <description> meta data.
These information elements are used by search engines to promote your website.
They are automatically generated based on page title & content, but you can
finetune them. Make sure they fit the content of the page, otherwise you will
be downgraded by search engines.
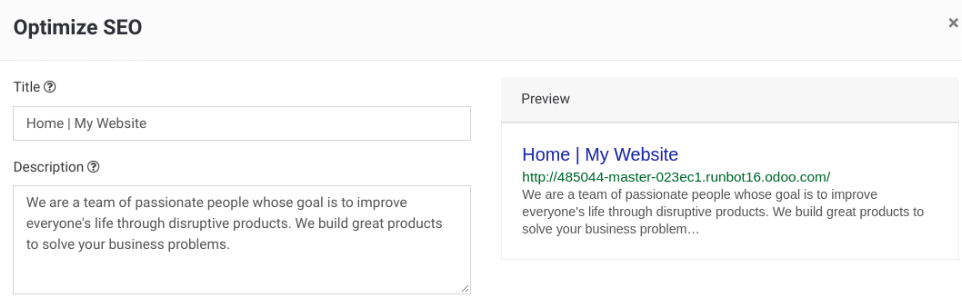
Keywords
In order to write quality content and boost your traffic, Odoo provides
a <keyword> finder. Those keywords are the searches you want to head
towards your website. For each keyword, you see how it is used in the content
(H1, H2, page title, page description, page content) and what are the related
searches in Google. The more keywords are used the better.
If your website is in multiple languages, you can use the Promote tool for every language of a single page and set specific title, description and search tags.
Content is King
When it comes to SEO, content is usually king. Odoo provides several modules to help you build your website content:
Odoo Blogs: write great contents.
Odoo Slides: publish all your Powerpoint or PDF presentations. Their content is automatically indexed on the web page. Example: odoo.com/slides/public-channel-1
Odoo Forum: let your community create contents for you. Example: odoo.com/forum/1 (accounts for 30% of Odoo.com landing pages)
Odoo Mailing List Archive: publish mailing list archives on your website. Example: odoo.com/groups/community-59 (1000 pages created per month)
The 404 page is a regular page, that you can edit like any other page in Odoo. That way, you can build a great 404 page to redirect to the top content of your website when visitors get lost in invalid URLs.
Use Social Networks
Social media is built for mass sharing. If lots of people share your content on social media, then it’s likely more people will link to it, and links are a huge factor for SEO ranking.
Odoo embeds several tools to share content through social media:
Social Network
Odoo allows to link all your social network accounts in your website footer. All you have to do is to refer all your accounts in your company settings.
Social Share
Drop the building block Share on any page you want your visitors to share. By clicking the icon, they are prompted to share the page in their social media wall.
Most social media use a picture of the picture to decorate the share post. Odoo uses the website logo by default but you can choose any other image of your page in the Promote tool.
Facebook Page
Drop the building block Facebook Page to display a widget of your Facebook business page and encourage visitors to follow it. You can display the timeline, the next events and the messages.
Twitter Scroller
Display the Twitter feeds with customer satifaction on your website. This will increase the number of tweets and shares.
URLs Handling
This section sheds some light on how Odoo makes URLs SEO-friendly.
URLs Structure
A typical Odoo URL will look like this
https:// = Protocol
www.mysite.com = your domain name
/fr_FR = page language. This part of the URL is removed if the visitor browses the main language of the website.
/shop/product = every module defines its own namespace (/shop is for the catalog of the eCommerce module, /shop/product is for a product page).
my-great-product = by default, this is the slugified title of the product this page refers to. But you can customize it for SEO purposes. A product named “Pain carré” will be slugified to “pain-carre”. Depending on the namespace, this could be different objects (blog post, page title, forum post, forum comment, product category, etc.).
-31 = the unique ID of the product
Note that any dynamic component of an URL can be reduced to its ID.
Some URLs have several dynamic parts, like this one (a blog category and a post):
In the above example:
Company News is the title of the blog
The Odoo Story is the title of a specific blog post
When an Odoo page has a pager, the page number is set directly in the URL (does not have a GET argument). This allows every page to be indexed by search engines. Example:
HTTPS
Search engines boost ranking of secure HTTPS/SSL websites. So, by default all Odoo Online instances are fully based on HTTPS. If the visitor accesses your website through a non HTTPS url, it gets a 301 redirect to its HTTPS equivalent.
Multi-Language Support
Multi-Language URLs
If you run a website in multiple languages, the same content will be available in different URLs, depending on the language used.
You can even have several variations of the same language: pt_BR (Portuguese from Brazil) , pt_PT (Portuguese from Portugal).
Language Annotation
To let search engines know that the second URL is the French translation of the first URL, Odoo will add an HTML link element in the header. In the HTML <head> section of the main version, Odoo automatically adds a link element pointing to the translated versions of that webpage;
With this approach:
Search engines will redirect to the right language according to the visitor language.
You do not get penalized by search engines if your page is not translated yet. Indeed, it’s not a duplicated content, but a different version of the same content.
Language Detection
When a visitor lands for the first time on your website (e.g. yourwebsite.com/shop), they may automatically be redirected to a translated version according to their browser language preference (e.g. yourwebsite.com/fr_FR/shop).
Next time, it keeps a cookie of the current language to avoid any redirection.
To force a visitor to stick to the default language, you can use the code of the default language in your link, example: yourwebsite.com/en_US/shop. This will always land visitors to the English version of the page, without using the browser language preferences.
Page Speed
Introduction
The time to load a page is an important criteria for search engines. A faster website not only improves your visitor’s experience, but gives you a better page ranking. Some studies have shown that, if you divide the time to load your pages by two (e.g. 2 seconds instead of 4 seconds), the visitor abandonment rate is also divided by two. (25% to 12.5%). One extra second to load a page could cost $1.6b to Amazon in sales.
Fortunately, Odoo does all the magic for you. Below, you will find the tricks Odoo uses to speed up your page loading time. You can compare how your website ranks using these two tools:
Images
When you upload new images, Odoo automatically compresses them to reduce their sizes (lossless compression for .PNG and .GIF and lossy compression for .JPG).
From the upload button, you have the option to keep the original image unmodified if you prefer to optimize the quality of the image rather than performance.
Odoo compresses images when they are uploaded to your website, not when requested by the visitor. Thus, it’s possible that, if you use a third-party theme, it will provide images that are not compressed efficiently. But all images used in Odoo official themes have been compressed by default.
When you click on an image, Odoo shows you the Alt and title attributes of the <img> tag. You can click on it to set your own title and Alt attributes for the image.

Odoo’s pictograms are implemented using a font (Font Awesome in most Odoo themes). Thus, you can use as many pictograms as you want in your page, they will not result in extra requests to load the page.
Static Resources: CSS
All CSS files are pre-processed, concatenated, minified, compressed and cached (server-side and browser-side). The result:
only one CSS file request is needed to load a page
this CSS file is shared and cached amongst pages, so that when the visitor clicks on another page, the browser doesn’t have to even load a single CSS resource.
this CSS file is optimized to be small
Pre-processed: The CSS framework used by Odoo is Bootstrap. Although a theme might use another framework, most of Odoo themes extend and customize Bootstrap directly. Since Odoo supports Less and Sass, you can modify CSS rules instead of overwriting them through extra CSS lines, resulting in a smaller file.
Concatenated: every module or library you might use in Odoo has its own set of CSS, Less or Sass files (eCommerce, blogs, themes, etc.). Having several CSS files is great for the modularity, but not good for the performance because most browsers can only perform 6 requests in parallel resulting in lots of files loaded in series. The latency time to transfer a file is usually much longer than the actual data transfer time, for small files like .JS and .CSS. Thus, the time to load CSS resources depends more on the number of requests to be done than the actual file size.
To address this issue, all CSS / Less / Sass files are concatenated into a single .CSS file to send to the browser. So a visitor has only one .CSS file to load per page, which is particularly efficient. As the CSS is shared amongst all pages, when the visitor clicks on another page, the browser does not even have to load a new CSS file!
The CSS sent by Odoo includes all CSS / Less / Sass of all pages / modules. By doing this, additional page views from the same visitor will not have to load CSS files at all. But some modules might include huge CSS/Javascript resources that you do not want to prefetch at the first page because they are too big. In this case, Odoo splits this resource into a second bundle that is loaded only when the page using it is requested. An example of this is the backend that is only loaded when the visitor logs in and accesses the backend (/web).
If the CSS file is very big, Odoo will split it into two smaller files to avoid the 4095 selectors limit per sheet of Internet Explorer. But most themes fit below this limit.
Minified: After being pre-processed and concatenated, the resulting CSS is minified to reduce its size.
The final result is then compressed, before being delivered to the browser.
Then, a cached version is stored server-side (so we do not have to pre-process, concatenate, minify at every request) and browser-side (so the same visitor will load the CSS only once for all pages they visit).
Static Resources: Javascript
As with CSS resources, Javascript resources are also concatenated, minified, compressed and cached (server-side and browser-side).
Odoo creates three Javascript bundles:
One for all pages of the website (including code for parallax effects, form validation, etc.)
One for common Javascript code shared among frontend and backend (Bootstrap)
One for backend specific Javascript code (Odoo Web Client interface for your employees using Odoo)
Most visitors of your website will only need the first two bundles, resulting in a maximum of two Javascript files to load to render one page. As these files are shared across all pages, further clicks by the same visitor will not load any other Javascript resource.
If you work on developer mode, the CSS and Javascript are neither concatenated, nor minified. Thus, it’s much slower. But it allows you to easily debug with the Chrome debugger as CSS and Javascript resources are not transformed from their original versions.
CDN
If you activate the CDN feature in Odoo, static resources (Javascript, CSS, images) are loaded from a Content Delivery Network. Using a Content Delivery Network has three advantages:
Load resources from a nearby server (most CDN have servers in main countries around the globe)
Cache resources efficiently (no computation resources usage on your own server)
Split the resource loading on different services allowing to load more resources in parallel (since the Chrome limit of 6 parallel requests is by domain)
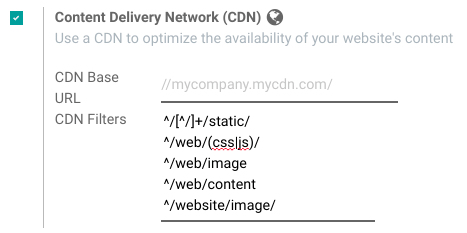
You can configure your CDN options from the Website Admin app, using the Configuration menu. Here is an example of configuration you can use:
HTML Pages
The HTML pages can be compressed, but this is usually handled by your web server (NGINX or Apache).
The Odoo Website builder has been optimized to guarantee clean and short HTML code. Building blocks have been developed to produce clean HTML code, usually using Bootstrap and the HTML editor.
As an example, if you use the color picker to change the color of a paragraph to the primary color of your website, Odoo will produce the following code:
<p class="text-primary">My Text</p>
Whereas most HTML editors (such as CKEditor) will produce the following code:
<p style="color: #AB0201">My Text</p>
Responsive Design
Websites that are not mobile-friendly are negatively impacted in search engine rankings. All Odoo themes rely on Bootstrap to render efficiently according to the device: desktop, tablet or mobile.
As all Odoo modules share the same technology, absolutely all pages in your website are mobile friendly.
Browser Caching
Javascript, images and CSS resources have an URL that changes
dynamically when their content change. As an example, all CSS files are
loaded through this URL:
localhost:8069/web/content/457-0da1d9d/web.assets_common.0.css.
The 457-0da1d9d part of this URL will change if you modify the CSS of
your website.
This allows Odoo to set a very long cache delay (XXX) on these resources: XXX secs, while being updated instantly if you update the resource.
Scalability
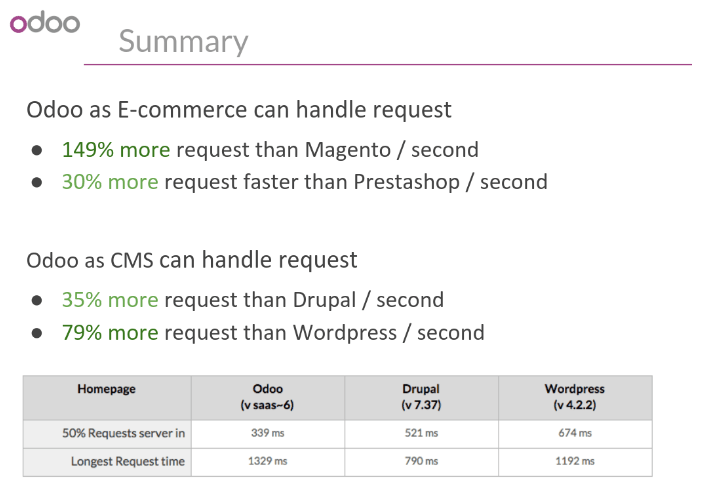
In addition to being fast, Odoo is also more scalable than traditional CMS and eCommerce (Drupal, Wordpress, Magento, Prestashop). The following link provides an analysis of the major open source CMS and eCommerce compared to Odoo when it comes to high query volumes: https://www.odoo.com/slides/slide/197
Here is the slide that summarizes the scalability of Odoo Website & eCommerce.
Search Engines Files
Sitemap
The sitemap points out pages to index to search engine robots.
Odoo generates a /sitemap.xml file automatically for you. For
performance reasons, this file is cached and updated every 12 hours.
By default, all URLs will be in a single /sitemap.xml file, but if you
have a lot of pages, Odoo will automatically create a Sitemap Index
file, respecting the sitemaps.org
protocol grouping sitemap
URL’s in 45000 chunks per file.
Every sitemap entry has 4 attributes that are computed automatically:
<loc>: the URL of a page<lastmod>: last modification date of the resource, computed automatically based on related object. For a page related to a product, this could be the last modification date of the product or the page.<priority>: modules may implement their own priority algorithm based on their content (example: a forum might assign a priority based on the number of votes on a specific post). The priority of a static page is defined by it’s priority field, which is normalized (16 is the default).
Structured Data Markup
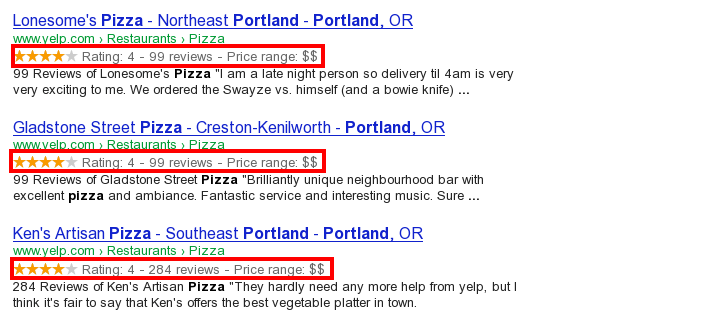
Structured Data Markup is used to generate Rich Snippets in search engine results. It is a way for website owners to send structured data to search engine robots; helping them understand your content and create well-presented search results.
Google supports a number of rich snippets for content types, including: Reviews, People, Products, Businesses, Events and Organizations.
Odoo implements micro data as defined in the schema.org specification for events, eCommerce products, forum posts and contact addresses. This allows your product pages to be displayed in Google using extra information like the price and rating of a product:
robots.txt
When indexing your website, search engines take a first look at the general indexing rules of the a``/robots.txt`` file (allowed robots, sitemap path, etc.). Odoo automatically creates it. Its content is:
User-agent: * Sitemap: https://www.odoo.com/sitemap.xml
It means that all robots are allowed to index your website and there is no other indexing rule than specified in the sitemap to be found at following address.
You can customize the file robots in developer mode from Settings –> Technical –> User Interface –> Views (exclude robots, exclude some pages, redirect to a custom Sitemap). Make the Model Data of the view Non Updatable to not reset the file after system upgrades.

